|
|
|
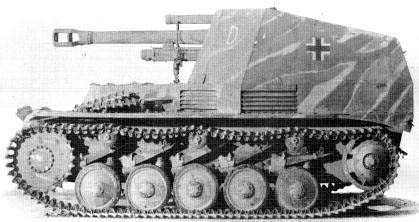
Wespe

German
Wespe - Sd. Kfz. 124
Entering service in 1936 , the Panzerkamfwagen II served as Germany's main battle tank during the Polish and French campaigns but , on the Eastern Front , it was hopelessly outclassed by the Russian heavy tanks . Consequently , the PzKpfw II was retired from the the front lines and it's chassis used in the production of the new assault guns : Wespe and Marder.
Wespe was designed by Alkett ( Berlin ) in mid 1942 and was produced by Famo in Breslau and Vereinigte Maschinenwerke in Warsaw . Wespe was to use regular and modified PzKpfw II Ausf F chassis . Early versions of Wespe were based on regular tank chassis with the engine moved forward to a more central location and reinforced suspension in order to absorb the stress from firing recoil . Late versions were based on modified chassis with a slightly lengthened hull , engine and radiators moved forward and an even more reinforced suspension . The modified chassis was known as Geschutzwagen ( Gun Carriage ) II . The configuration of the driver compartment was changed during production , creating two variants as well.
Wespe was armed with a 105mm light field howitzer ( leFH 18 ) , which was the mainstay of all artillery regiments during the war . The 105mm leFH 18 was able to fire high explosives , shaped charges and armour piercing ammunition and had an effective range of 8400 meters . The gun was mounted in the center of an open-topped armoured superstructure over the engine and behind a gun shield . The tall superstructure was made up of 10mm armor plates , which provided limited protection for the crew and storage for 32 rounds of ammunition . The space inside the superstructure was cramped and there was not much space left to operate the gun . A machine gun ( 7.92mm MG34 ) and a submachine gun ( 9mm MP38 or MP40 ) were issued to the crew and carried inside the fighting compartment for local defence.
The main idea behind the design of Wespe was to provide all mobile formations with indirect artillery support . Wespe units were to operate behind the frontlines and were not to engage enemy vehicles , however they carried armour-piercing ammunition in case of an encounter . Like artillery , Wespe vehicules operated in batteries and received orders and directions from forward observers by radio or field telephone reducing the risk of being exposed to direct enemy fire.
From February 1943 to August 1944 , 676 Wespe along with 159 ammunition carriers were produced . The ammunition carriers ( designated Munitions Sf auf Fgst PzKpfw II ) were regular Wespes without the main armament . They could carry 90 rounds of ammunition and were used to supply Wespe batteries with ammunition in the field.
Wespe was issued to Panzer division's artillery batteries starting in spring of 1943 . Each battery had six Wespe and two Wespe ammo carriers . Wespe's first major action was at Kursk in July 1943 , where it proved to be very effective and afterwards saw active service on all fronts until the end of the war . Despite their weak armor there were still some 307 Wespe in service as of March 1945.
By Pz_Tobruk
.
Crew: 5 (commander, 3 gunners, and radio operator)
Weight: 11.0 tons
Dimensions: 4.81 x 2.28 x 2.30
Armor (max):20-30mm
Range: 95 km
Speed (max):20.0 km/hr
Main gun: 105 mm L/26
No. Produced: 676
.
